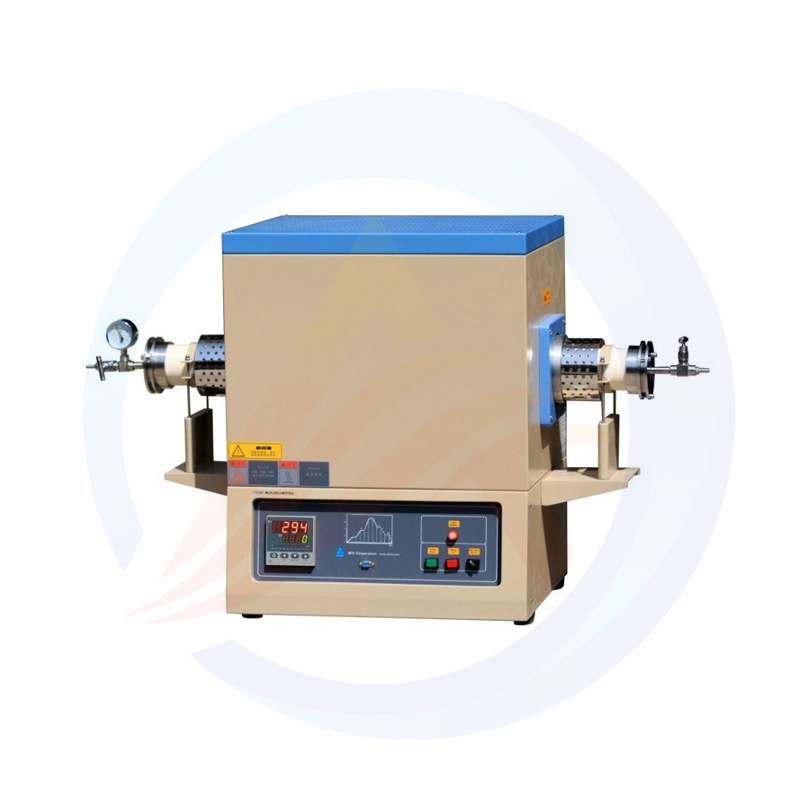
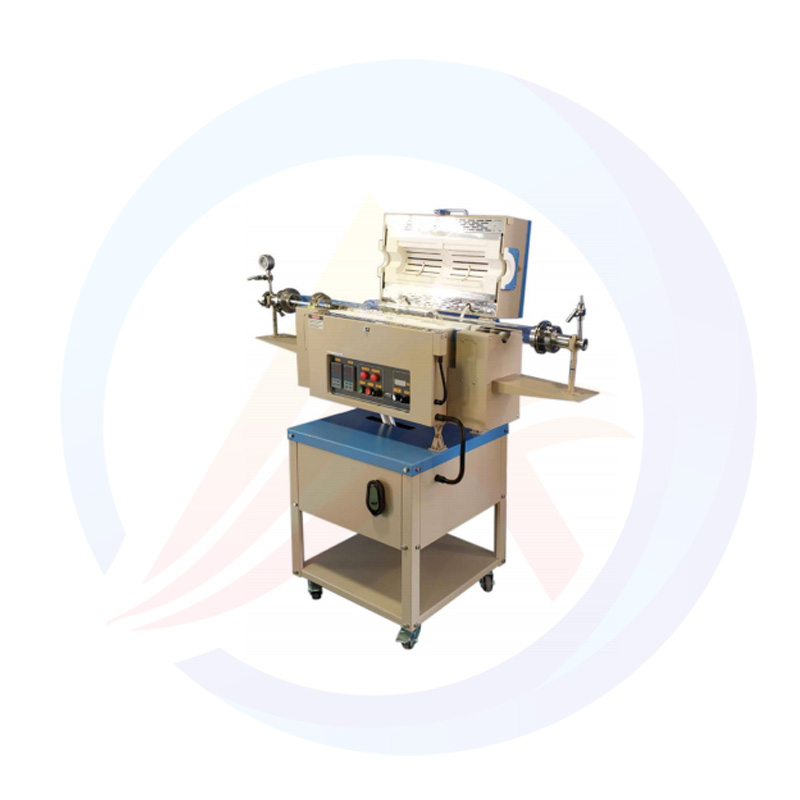
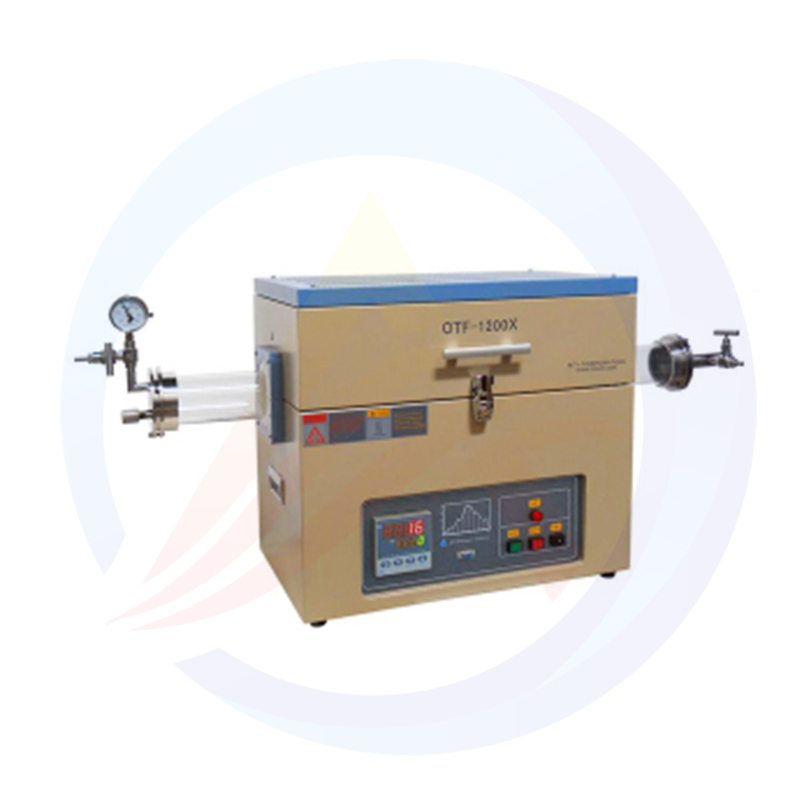
What is a laboratory furnace?
A laboratory furnace, also known as a lab furnace or scientific furnace, is a specialized piece of equipment used in scientific research and industrial laboratories for various heat-treating applications. It is designed to provide precise control over temperature, atmosphere, and other parameters to enable researchers and engineers to perform experiments and processes under carefully controlled conditions.

Here are some key features and uses of a laboratory furnace:
1. Temperature Control:
Laboratory furnaces are equipped with advanced temperature control systems that allow for precise and accurate temperature settings. These systems can maintain temperatures ranging from room temperature to extremely high temperatures, depending on the specific furnace model and design.
2. Atmosphere Control:
Some laboratory furnaces offer the ability to control the atmosphere inside the chamber, such as by purging with inert gases like argon or nitrogen. This is important for processes that require a specific gas environment to prevent oxidation, combustion, or other unwanted reactions.
3.Versatility:
Laboratory furnaces can be used for a wide range of applications, including annealing, sintering, heat treatment, ashing, calcination, and material synthesis. They can accommodate various types of samples and materials, including metals, ceramics, glass, plastics, and biological specimens.
4. Chamber Design:
The chamber of a laboratory furnace can vary in size, shape, and construction material depending on the intended application. Some furnaces have rectangular chambers for easy sample placement and removal, while others may have specialized chambers for specific types of experiments.
5. Safety Features:
Laboratory furnaces are designed with safety in mind, featuring over-temperature protection, automatic shut-off systems, and other safety mechanisms to prevent accidents and protect users.
Automation and Programming:
Many modern laboratory furnaces are equipped with automation and programming capabilities, allowing users to set up complex temperature profiles and sequences of operations. This enables researchers to conduct experiments with minimal manual intervention and improves reproducibility and accuracy.
Industry Standards:
Laboratory furnaces are often designed to meet specific industry standards and certifications, such as CE, UL, or ISO, to ensure their quality, safety, and reliability.
In summary, a laboratory furnace is a vital tool in scientific research and industrial laboratories, providing precise control over temperature, atmosphere, and other parameters to enable a wide range of heat-treating applications.

What is furnace used for?
A furnace is a device used for heating materials to high temperatures, typically for industrial, commercial, or residential purposes. The specific uses of a furnace can vary widely depending on its design, size, and intended application. Here are some common uses of furnaces:
1. Metal Processing:
Furnaces are widely used in the metal industry for processes such as smelting, refining, annealing, hardening, and tempering. They are essential for transforming raw materials into finished products, such as steel, aluminum, and other metals.
2. Glass and Ceramics Manufacturing:
Furnaces play a crucial role in the production of glass and ceramics. They are used to melt raw materials, shape them into desired forms, and then anneal or harden the finished products.
3. Heat Treatment:
Furnaces are used for various heat treatment processes, such as quenching, tempering, and normalizing, to alter the physical and mechanical properties of metals and other materials.
4. Chemical Processing:
Furnaces are employed in the chemical industry for processes like calcination, pyrolysis, and combustion. They are used to heat chemicals to high temperatures to initiate chemical reactions or change their properties.
5. Waste Incineration:
Furnaces are sometimes used for waste incineration, where waste materials are burned at high temperatures to reduce their volume and destroy harmful substances.
6. Residential Heating:
In residential settings, furnaces are used to heat homes and buildings. They burn fuel, such as natural gas or oil, to generate heat that is distributed through the building's heating system.
7. Industrial Heating:
Furnaces are also used in industrial settings for various heating applications, such as drying, curing, and sterilizing. They can be customized to meet the specific needs of different industries and processes.
8. Research and Development:
In scientific research and development, furnaces are used to conduct experiments and processes under carefully controlled conditions. They enable researchers to study the behavior of materials at high temperatures and develop new technologies and products.
In summary, furnaces are versatile devices that are used for a wide range of heating and processing applications in various industries and settings.

What does a lab muffle furnace do?
A lab muffle furnace, also known as a box furnace or a laboratory furnace, is a specialized type of furnace designed for use in laboratory settings. Its primary function is to provide a controlled, high-temperature environment for various scientific and research purposes.
Here are some specific tasks that a lab muffle furnace can perform:
Material Annealing: It can be used to anneal materials, a process that involves heating them to a specific temperature and then slowly cooling them to relieve internal stresses and improve their physical properties.
Sintering: Sintering is a process where particles of a material are fused together at high temperatures to form a solid mass with increased strength and density. A lab muffle furnace provides the necessary heat for this process.
Ashing and Drying: It can be utilized for ashing organic materials to remove combustible components and leaving behind the inorganic residue. Additionally, it can be used for drying samples or materials by removing moisture or solvents.
Material Characterization: Researchers can use a lab muffle furnace to study the behavior of materials at high temperatures. This includes observing changes in properties such as phase transitions, melting points, and thermal expansion.
Ceramic and Glass Processing: Small-scale production or testing of ceramics and glass materials can be carried out in a lab muffle furnace. It allows for precise control of the heating and cooling rates, which is crucial for obtaining desired properties in these materials.
Heat Treatment of Metals: Although primarily used for non-metallic materials, some lab muffle furnaces are designed to handle metals for heat treatment processes like quenching, tempering, or normalizing in controlled environments.
Synthesis of Materials: In chemistry and materials science, lab muffle furnaces are employed for the synthesis of new materials or compounds that require high temperatures.
Environmental Simulation: Researchers can use the controlled environment of a lab muffle furnace to simulate extreme conditions, such as high temperatures found in natural environments or industrial processes.
The key features of a lab muffle furnace include its ability to provide precise temperature control, a sealed chamber that minimizes heat loss and contamination, and a variety of programmable heating and cooling profiles to meet specific experimental requirements.