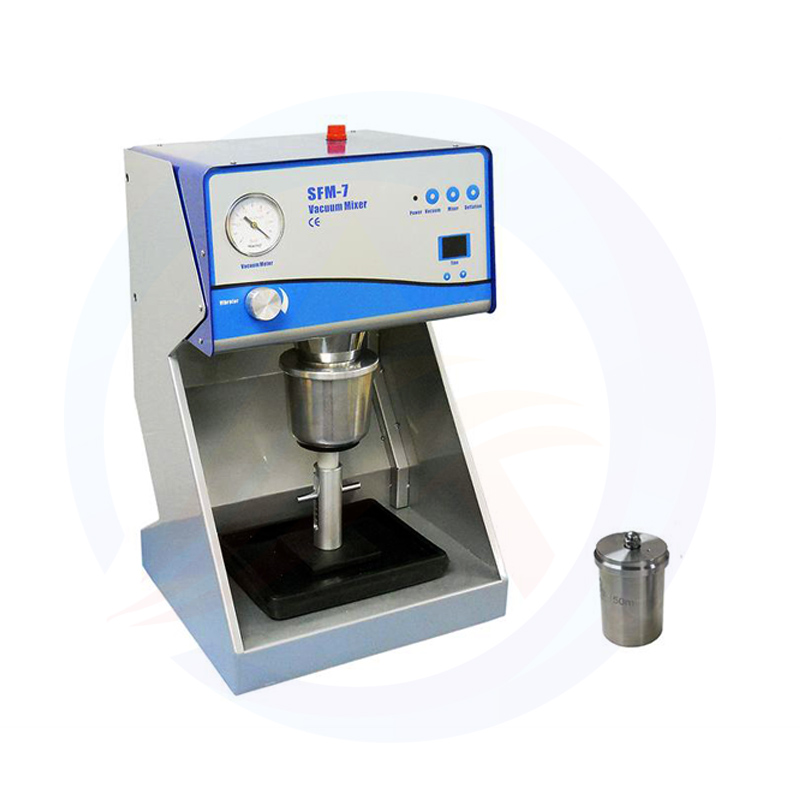
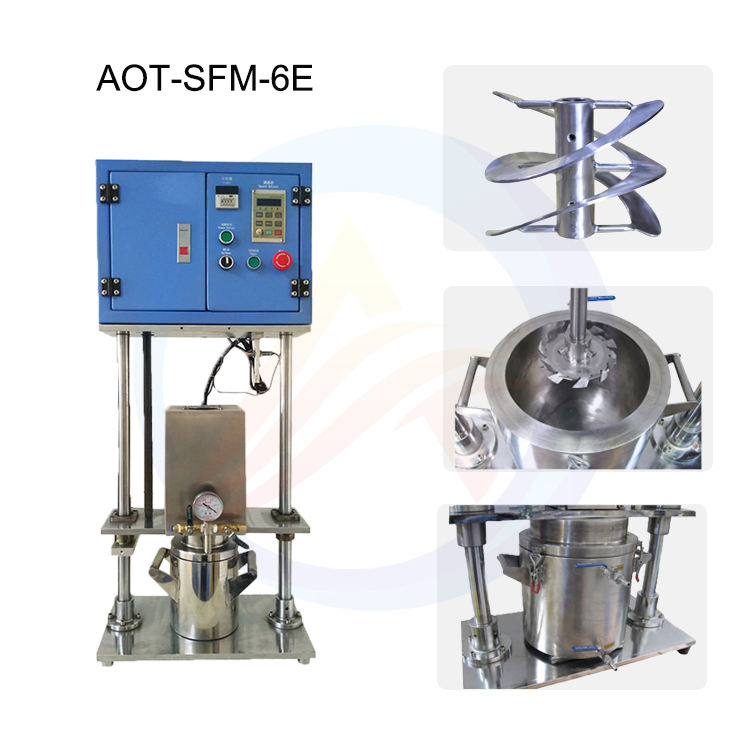
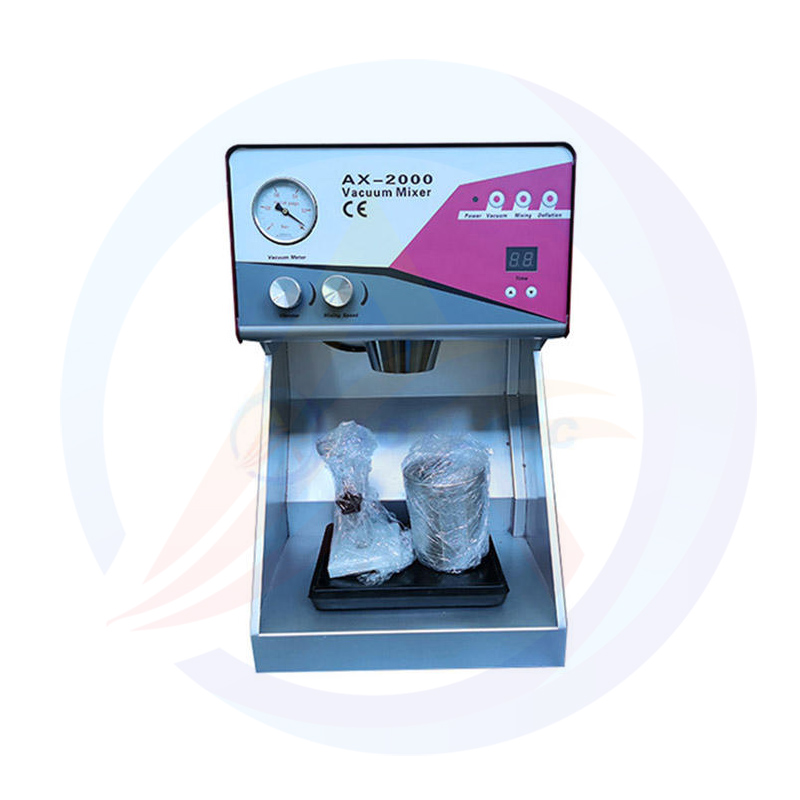
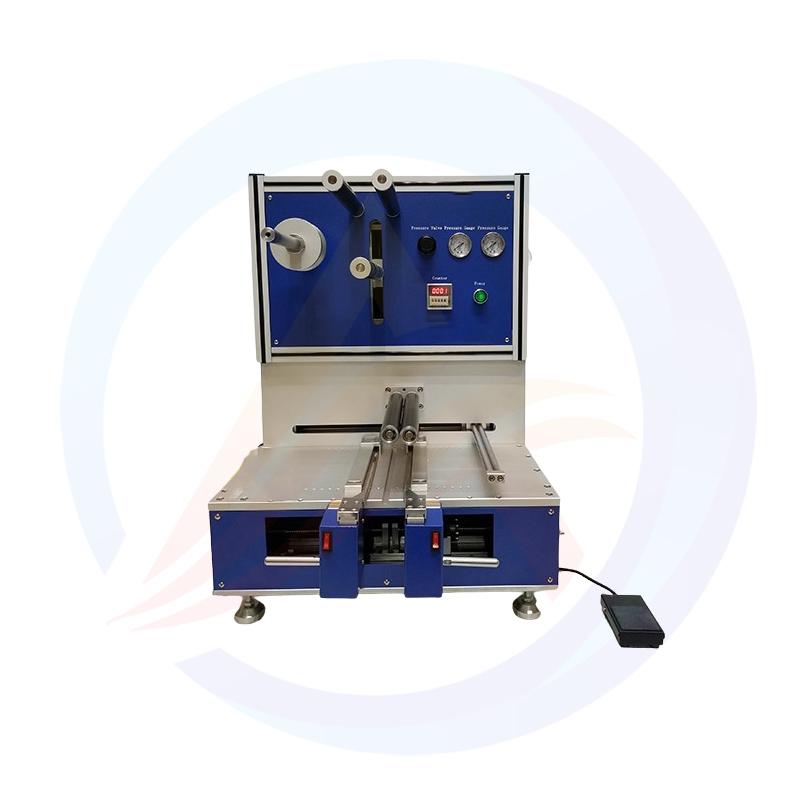
What is the lithium battery slitting machine?
What is the process of electrode slitting?
Electrode slitting is a process used in the manufacturing of lithium-ion batteries to create thinner electrodes with precise dimensions. The slitting process involves cutting a larger electrode material into narrower strips that are suitable for use in battery cells. Here's a general overview of the electrode slitting process:
1. Material selection: The first step is to select the appropriate electrode material based on the battery chemistry requirements. Typically, lithium-ion batteries use materials such as graphite for the anode and lithium metal oxides (e.g., lithium cobalt oxide) for the cathode.
2. Coating: The electrode material is usually coated on a thin metal foil, such as copper or aluminum. The coating process involves applying a slurry containing active material particles, binders, conductive additives, and solvents onto the metal foil surface. This coated foil acts as the base for the electrodes.
3. Drying: After the coating, the wet electrode is passed through a drying process to remove the solvents, leaving behind a solid electrode layer. Drying can be achieved through various methods like oven-drying or infrared heating.
4. Slitting: Once the dried electrode is ready, it undergoes the slitting process. Slitting machines are used to cut the electrode-coated foil into narrower strips of the desired width. These machines use sharp blades or rotary cutters to make precise cuts.

5. Quality control: Throughout the slitting process, quality control measures are implemented to ensure the accuracy of the electrode dimensions. Various parameters, including width, thickness, and uniformity, are checked to meet the specified requirements.
6. Collection and storage: The sliced electrode strips are collected and sorted for further processing. They are typically wound into rolls or stacked for ease of handling and storage.
7. Assembly: The electrode strips are further processed and combined with other components, such as separators and electrolytes, to assemble battery cells.
It's important to note that the electrode slitting process is just one step in the overall battery manufacturing process, which involves additional stages like electrode stacking, cell assembly, and battery testing. The specific details and variations of the slitting process may vary depending on the battery manufacturer and technology used
What is the purpose of a slitting machine?
A slitting machine is used to cut large rolls of material into narrower strips, known as slits. The purpose of a slitting machine is to convert wide rolls or sheets of material into smaller, more usable widths. The machine typically consists of a set of circular blades or cutting wheels that rotate and create the desired slits in the material as it passes through the machine.
Slitting machines are commonly used in various industries such as paper manufacturing, plastic film production, metal processing, textiles, and packaging. They are employed to convert rolls of materials like paper, film, foil, fabric, or metal into narrower rolls suitable for further processing or packaging.
The slitting process is essential for several reasons, including:
1. Customization: Slitting allows manufacturers to produce materials in specific widths according to their customer's requirements. Different industries have different needs, and slitting machines enable the production of materials in various widths to meet those specific demands.
2. Efficiency: Wide rolls of materials are often more cost-effective to produce than narrow ones. By slitting a wide roll into smaller widths, manufacturers can maximize the utilization of the material. This can result in cost savings and increased efficiency in the production process.
3. Handling and Storage: Slitting materials into narrower widths makes them easier to handle and store. Smaller rolls are lighter, more manageable, and occupy less space. This simplifies transportation, storage, and handling processes within the manufacturing facility or during distribution.
4. Secondary Processing: Slitting is often a precursor to other manufacturing processes. The narrower slit rolls can be used in subsequent processes such as printing, laminating, coating, or converting into final products.
Overall, the purpose of a slitting machine is to convert wide rolls or sheets of material into narrower strips, enabling customization, efficiency, improved handling, and facilitating further processing in various industries.
What are the different types of slitting machines?
Slitting machines are used in various industries to cut wide rolls of material into narrower strips. There are several types of slitting machines available, each designed to meet specific requirements. Here are some common types:

1. Rotary Slitter: This is the most common type of slitting machine. It consists of one or multiple circular blades mounted on a rotating shaft. The material passes through the blades, which cut it into narrower strips. Rotary slitters can handle a wide range of materials, including paper, plastic, films, and metal foils.
2. Crush Slitter: Crush slitting is a method where the material is pressed against a hardened roller or a blade under high pressure. The pressure causes the material to deform and break along the desired cutting line. Crush slitting is suitable for materials that are relatively soft and flexible.
3. Razor Slitter: Razor slitting machines use sharp razor blades to cut through the material. The blades are mounted on a holder and positioned against an anvil roll. As the material passes between the blade and the anvil roll, it is sliced into narrower strips. Razor slitting is commonly used for thin films, adhesive tapes, and delicate materials.
4. Shear Slitter: Shear slitting machines employ a pair of circular blades that move in opposite directions to cut the material. The blades have a scissor-like action and smoothly shear through the material, maintaining a clean cut edge. Shear slitting is often used for heavier and thicker materials, such as plastics, rubber, and non-woven fabrics.
5. Score Slitter: A score slitter uses a scoring technique to partially cut the material rather than completely severing it. The machine creates a score line that weakens the material, making it easier to tear along the desired line. Score slitting is commonly used for paper, cardboard, and packaging materials.
6. Laser Slitter: Laser slitting machines use high-powered lasers to cut through the material. The laser beam is guided by computer-controlled optics, allowing precise and intricate cuts. Laser slitting is suitable for a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, fabrics, and composites.
These are some of the commonly used types of slitting machines. The choice of machine depends on the specific requirements of the material being processed, such as thickness, flexibility, and desired cutting precision
What is the difference between slitting and cutting?
Slitting and cutting are similar processes used to separate or divide materials into narrower or smaller sections. While they have some similarities, there are important differences between the two processes.
Slitting:
Slitting is a process that involves cutting a large roll or sheet of material into narrower strips. It is commonly used for materials such as paper, plastic films, metal coils, fabrics, and other flexible or thin materials. The slitting machine usually consists of rotary knives or blades that make multiple parallel cuts along the width of the material, resulting in several narrower strips called "slits." Slitting is often used in industries such as packaging, printing, textiles, and metal processing to produce products like narrow tapes, labels, ribbons, and precision-cut materials.
Cutting:
Cutting, on the other hand, refers to the process of dividing a material into smaller pieces or shapes. It involves removing a part of the material to separate it into distinct sections. Cutting can be performed using various methods, such as shearing, sawing, plasma cutting, laser cutting, waterjet cutting, or other specialized cutting tools or machinery. Cutting is commonly used in industries like manufacturing, construction, automotive, aerospace, and crafts, where materials need to be shaped or divided into specific sizes or geometries.
In summary, while slitting is specifically used to divide materials into narrower strips by making parallel cuts along their width, cutting is a broader term that encompasses various methods of separating materials into smaller pieces or shapes.