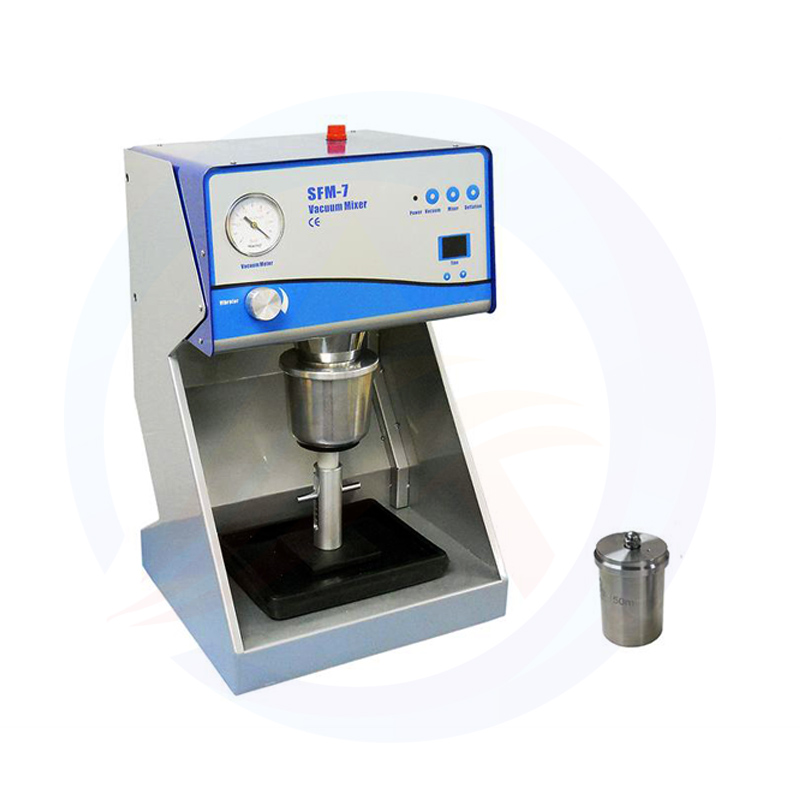
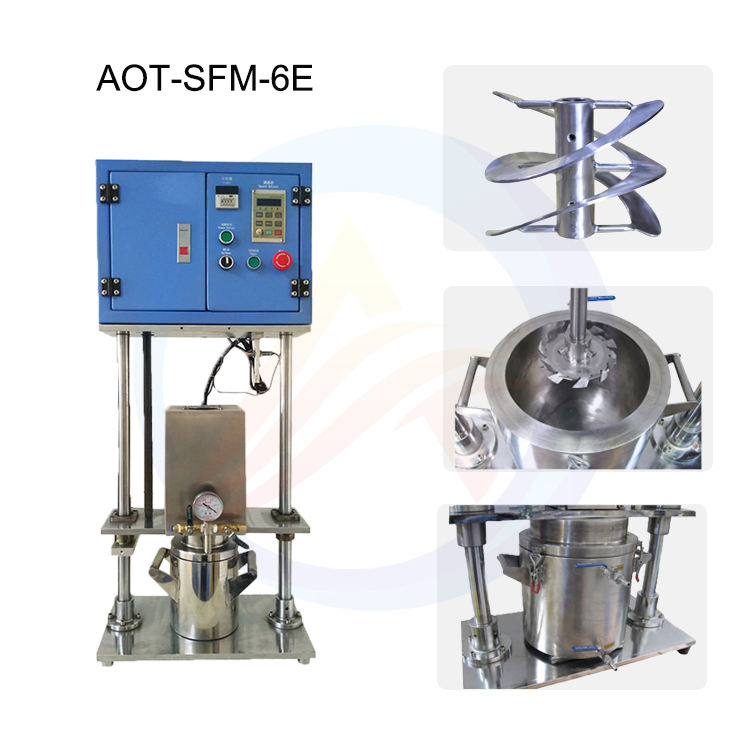
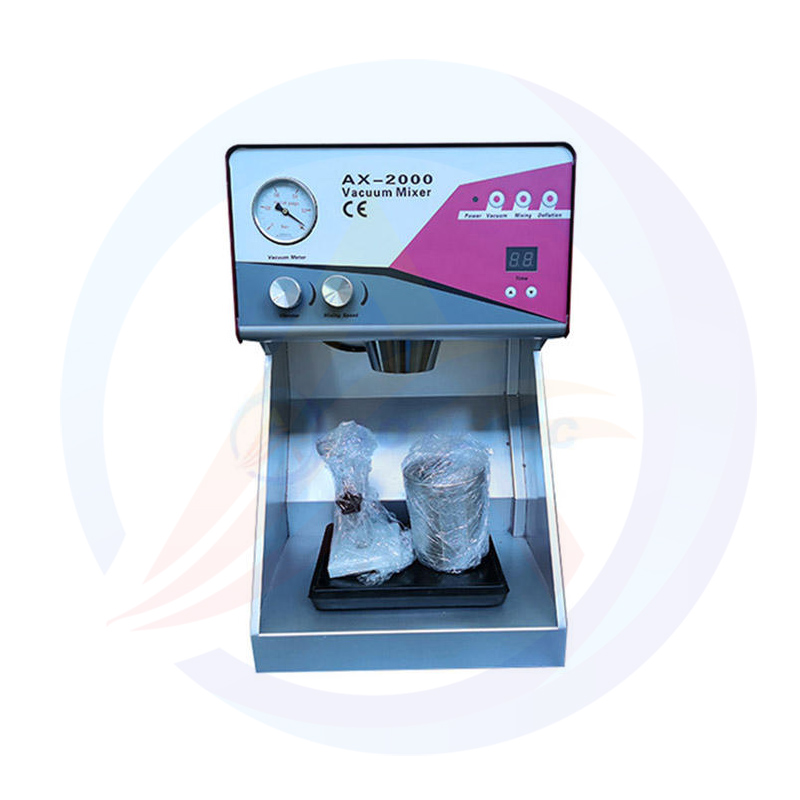
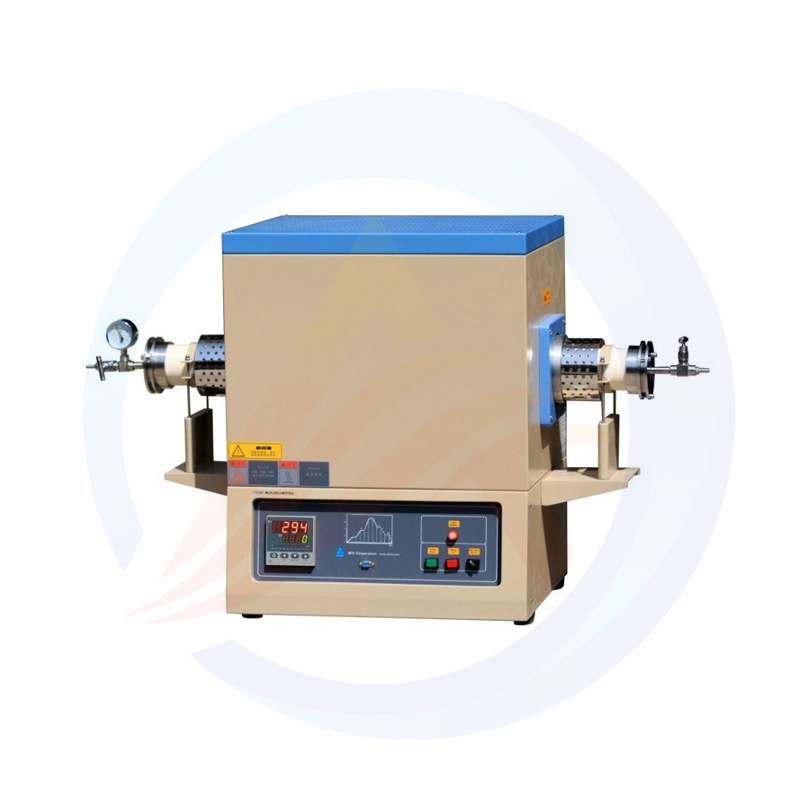
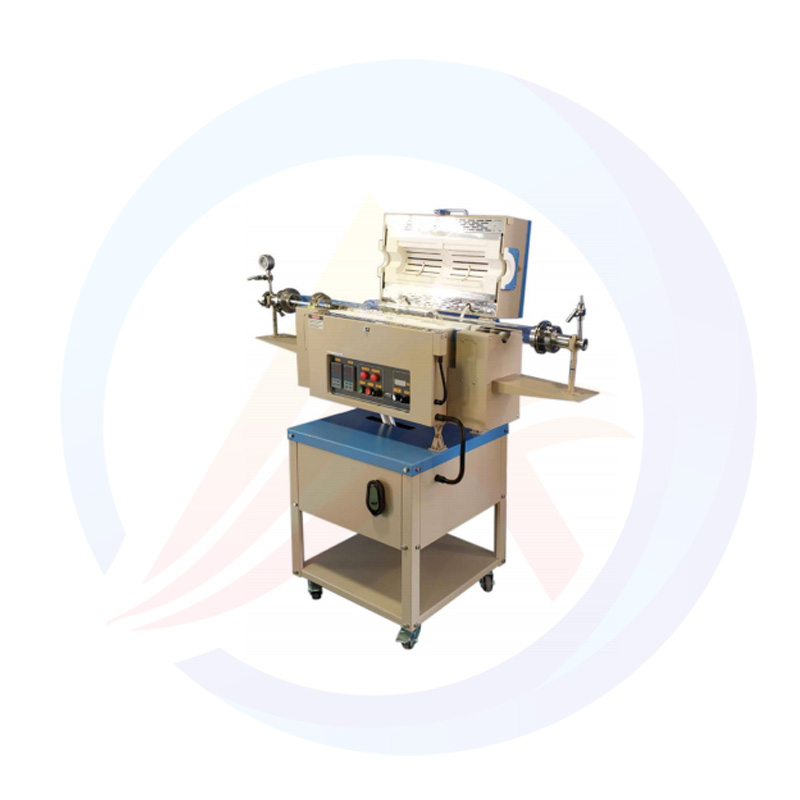
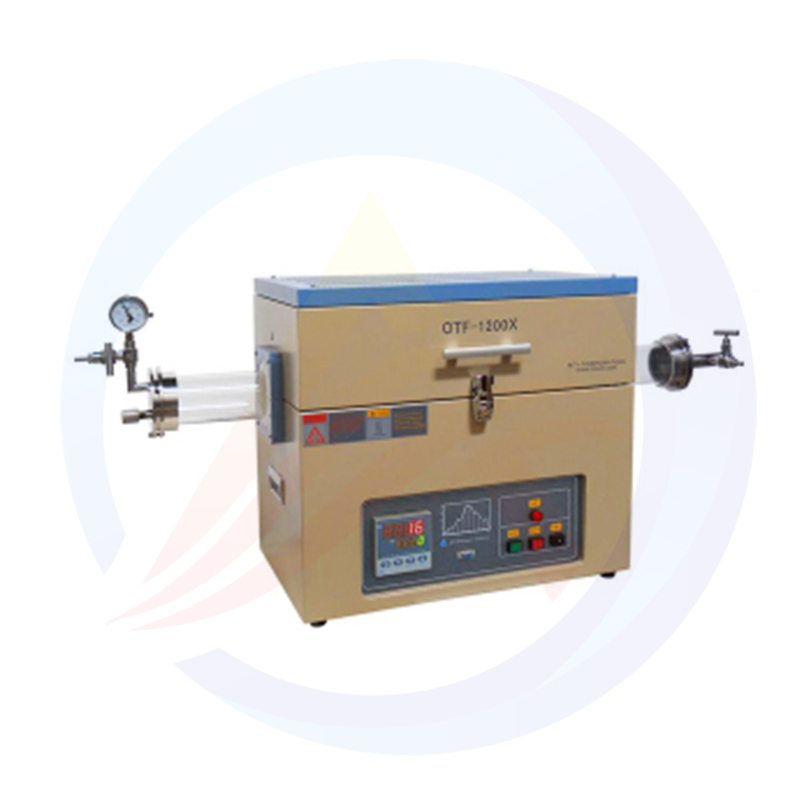
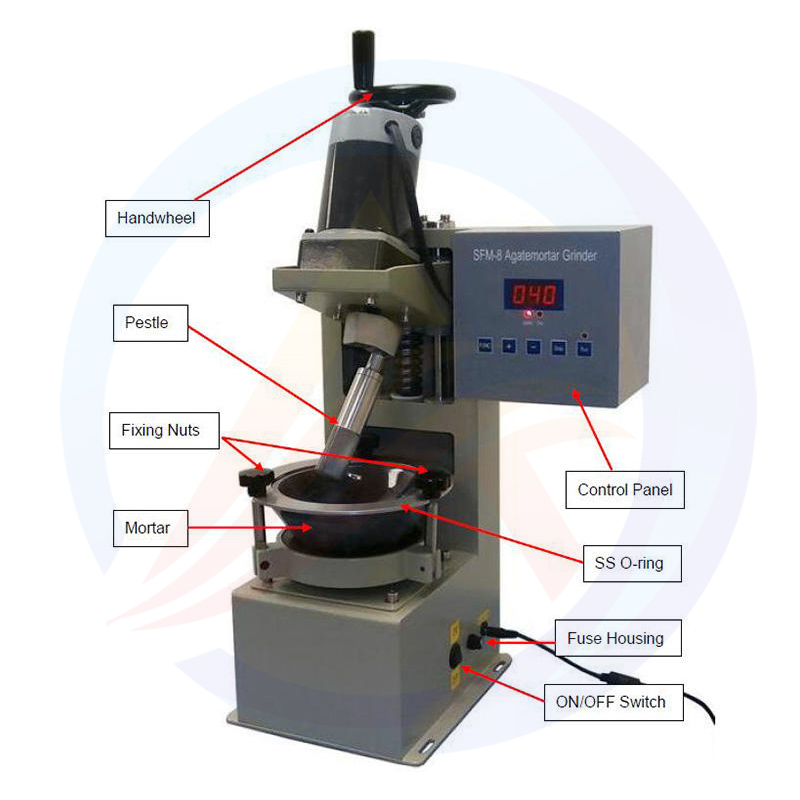
Lithium Battery Laboratory Ball Mill Introduction
The lithium battery laboratory ball mill is a specialized piece of equipment used for processing lithium battery materials in a laboratory setting. It is designed to efficiently grind, mix, and disperse various materials, making it an essential tool in the research and development of lithium batteries.
1. Applications
The lithium battery laboratory ball mill is widely used in the preparation of lithium battery materials, including positive and negative electrode materials, electrolytes, and separators. It can also be used for the recycling and processing of waste lithium batteries, contributing to environmental protection and sustainable development.
2. Structure and Components
The lithium battery laboratory ball mill is composed of several key components, including the grinding chamber, grinding balls, motor, and control system. The grinding chamber is where the material is placed for grinding, while the grinding balls provide the necessary force for grinding through their movement. The motor drives the grinding chamber and grinding balls to rotate, and the control system allows for precise adjustment of the grinding parameters.
3. Working Principle
The working principle of the lithium battery laboratory ball mill is based on the impact and friction between the grinding balls and the material. As the grinding chamber rotates, the grinding balls are carried along and strike the material, causing it to break down into smaller particles. The friction between the grinding balls and the walls of the grinding chamber also helps to refine the material further.
4.Operating Procedures
Before using the lithium battery laboratory ball mill, it is important to prepare the material and grinding balls according to the experimental requirements. The material should be weighed accurately and placed in the grinding chamber, along with the appropriate number and size of grinding balls. The grinding chamber is then sealed and the mill is started. The grinding parameters, such as speed, time, and temperature, can be adjusted as needed to achieve the desired grinding effect.
5. Safety Precautions
When operating the lithium battery laboratory ball mill, safety precautions must be taken to ensure the safety of personnel and equipment. Operators should wear protective equipment, such as safety glasses, gloves, and masks, to prevent injury from flying particles or dust. The mill should be operated in a well-ventilated area to avoid exposure to harmful fumes. Additionally, regular maintenance and inspections of the equipment are necessary to ensure its safe and reliable operation.
6. Advantages
The lithium battery laboratory ball mill offers several advantages, including high grinding efficiency, precise control of grinding parameters, and good dispersion of materials. It is also compact and easy to operate, making it an ideal choice for laboratory-scale research and development.

Usage of Lithium Battery Laboratory Ball Mill
Preparation and Inspection
Place the ball mill on a flat, stable surface.
Ensure the electrical connections are secure and there are no signs of damage or leakage.
Inspect the grinding chamber, grinding balls, and other components for any wear or damage.
Prepare the material to be grinded and ensure it is compatible with the ball mill.
Loading Material
Open the grinding chamber and place the prepared material and grinding balls inside.
Ensure that the material and grinding balls are loaded in the correct proportion.
Close the grinding chamber securely.
Setting Parameters
Use the control panel to set the desired grinding speed, time, and other parameters.
Ensure that the parameters are set according to the specific requirements of the experiment.
Starting the Ball Mill
Switch on the power and start the ball mill.
Gradually increase the speed to the desired level.
Monitor the grinding process closely and adjust the parameters if necessary.
Collecting the Sample
After the grinding process is complete, allow the ball mill to cool down.
Open the grinding chamber and carefully remove the grinded material.
Clean the grinding chamber and grinding balls for future use.
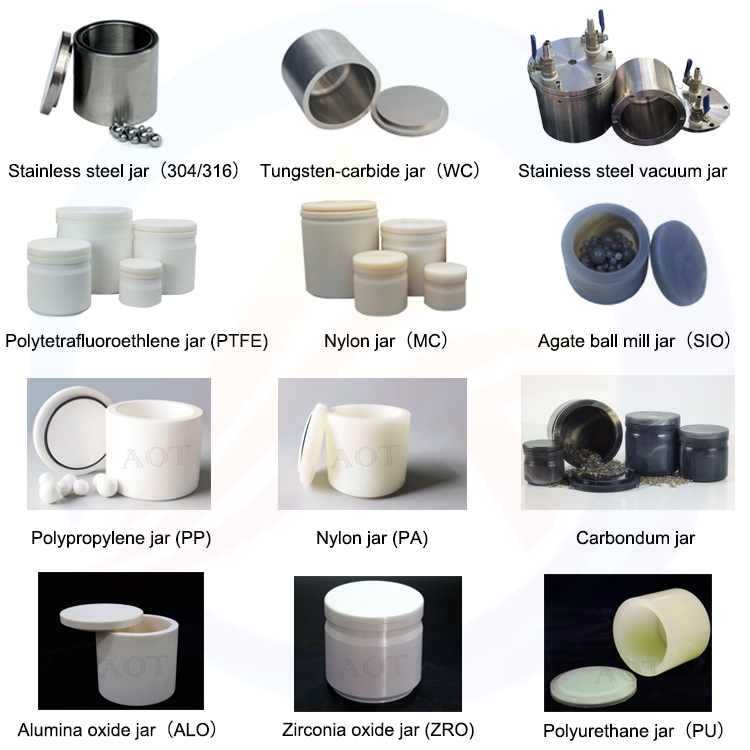


Precautions for Using Lithium Battery Laboratory Ball Mill
Safety First
Always wear protective equipment such as safety glasses, gloves, and masks when operating the ball mill.
Ensure that the area around the ball mill is clear of any obstacles and keep children and unauthorized personnel away.
Material Compatibility
Only use materials that are compatible with the ball mill to avoid damage to the equipment or injury to personnel.
Avoid using materials that may produce harmful fumes or explosives during grinding.
Correct Operation
Follow the manufacturer's instructions and operating manual closely to avoid misuse or damage to the equipment.
Do not overload the grinding chamber or use grinding balls that are too large or small for the chamber size.
Monitoring and Maintenance
Regularly monitor the grinding process and check for any signs of wear or damage to the equipment.
Perform regular maintenance such as cleaning and lubricating the moving parts to ensure smooth operation.
Replace worn-out components such as grinding balls and bearings as needed.
Electrical Safety
Ensure that the electrical connections are secure and there are no exposed wires or damaged sockets.
Use a grounded power outlet to avoid electrical shock hazards.
Avoid using the ball mill in wet or damp conditions to prevent electrical hazards.
Storage and Handling
Store the ball mill in a dry, well-ventilated area when not in use.
Handle the equipment with care to avoid dropping or damaging it.
Keep the equipment away from heat sources and flammable materials.
In the lithium battery laboratory ball mill experiments, if there is an accident, you should quickly take countermeasures according to the specific circumstances, the following are some common accidents and treatment methods:
1. Equipment failure
Equipment abnormal sound or vibration
Phenomenon: abnormal sound or excessive vibration when the equipment is running.
Treatment: immediately stop the machine to check, may be grinding media, samples or equipment components loose or damaged. Confirm that there is no problem and then restart the equipment, if the fault remains, you need to contact a professional for maintenance.
Power failure
Phenomenon: Sudden power failure or unstable power supply.
Treatment: Check whether the power plug, socket and power cord are intact, confirm that the power supply is stable before restarting the equipment. If the power can not be restored, you need to contact the laboratory manager or electrician to deal with it.
2. Sample Problems
Sample leakage or overflow
Phenomenon: Sample leaks or overflows from the ball mill during the grinding process.
Treatment: Immediately stop the machine, use appropriate tools or materials to clean up the leaked sample, to avoid contamination of the equipment and the experimental environment. Meanwhile, check the sealing of the ball mill jar to ensure that similar problems will not occur in the next experiment.
Uneven grinding of samples
Phenomenon: Uneven particle size distribution of the ground sample.
Treatment: Check whether the parameters such as grinding medium, grinding time and speed are set reasonably, adjust the parameters and grind again. If you still can not get a uniform sample after several attempts, you need to consider replacing the grinding media or equipment.
3. Safety issues
Fire or explosion
Phenomenon: Fire or explosion occurs in the equipment or experimental environment.
Treatment: Immediately cut off the power supply, use a fire extinguisher or fire fighting equipment to put out the fire, and quickly evacuate the experimental area. At the same time to the laboratory management personnel or the relevant departments to call the police for help, in accordance with the relevant requirements.
Injury to personnel
Phenomenon: Laboratory personnel are injured due to improper operation or equipment failure.
Treatment: Immediately stop the machine, the injured personnel to carry out preliminary first aid treatment, such as bleeding, bandage, etc.. At the same time, call the emergency telephone and send the injured personnel to the hospital for treatment.
4. Other accidents
Equipment shutdown
Phenomenon: equipment in the operation process suddenly stopped.
Treatment: Check whether the power supply, motor and transmission parts of the equipment are working normally, and then restart the equipment after confirming that there is no fault. If the operation cannot be resumed, it is necessary to contact professional personnel for maintenance.
Abnormal experimental data
Phenomenon: The experimental data does not meet the expectations or there are abnormal fluctuations.
Treatment: Check whether the experimental steps, parameter settings and data processing methods are correct, confirm that there is no error and then re-experiment. If the data are still abnormal after several experiments, it is necessary to analyze the reasons and adjust the experimental program.