01. The harm of moisture to lithium batteries
1. Battery swelling and leakage
If the water content of lithium-ion batteries is too much, it will chemically react with the lithium salt in the electrolyte and generate HF:
H2O + LiPF6 → POF3 + LiF + 2HF
Hydrofluoric acid (HF) is a highly corrosive acid that is very destructive to battery performance:
HF will corrode the metal parts inside the battery, the battery shell, and the seal, which will eventually cause the battery to break and leak.
HF damages the SEI membrane (Solid-Electrolyte Interface) inside the battery, reacting with the main components of the SEI membrane:
ROCO2Li + HF → ROCO2H + LiF
Li2CO3 + 2HF → H2CO3 + 2LiF
Finally, the LiF precipitation is generated inside the battery, so that the lithium ions in the battery negative plate irreversible chemical reaction, consumption of active lithium ions, the energy of the battery is reduced.
When the water is enough, the gas produced will be more, and the pressure inside the battery will become larger, which will cause the battery to be stressed and deformed, and there will be dangers such as battery bulge and leakage.
The situation of battery bulge and boot cover encountered in the use of mobile phones or digital electronic products on the market is mostly caused by high internal moisture and gas production bulge of lithium batteries.
2. The internal resistance of the battery increases
The internal resistance of the battery is one of the most important performance parameters of the battery, and it is the main sign to measure the difficulty of ion and electron transmission inside the battery, which directly affects the cycle life and operating state of the battery. The smaller the internal resistance, the less voltage occupied by the battery when discharging, and the more energy output.
When the water content increases, POF3 and LiF precipitation will occur on the surface of the battery SEI film (Solid-Electrolyte Interface), damaging the density and uniformity of the SEI film, resulting in a gradual increase in the internal resistance of the battery and a continuous decrease in the discharge capacity of the battery.
3. Cycle life shortened
The water content is too large, destroyed the battery SEI film, the internal resistance gradually increased, the battery discharge capacity is getting smaller and smaller, each time the battery is fully charged after the use of the battery is also getting shorter and shorter, the battery can be normally used to charge the number of discharge (cycle) will naturally become less, the battery's use time (life) will be shortened.
02. The source of water in the production of lithium batteries
In the manufacturing process of lithium batteries, the source of water can be divided into the following aspects:
1. The water brought in by raw materials
1.1 positive and negative electrode materials: positive and negative active substances are micron and nano particles, which can easily absorb water in the air; In particular, ternary or binary cathode materials with high Ni (nickel) content have large specific surface area, and the material surface is easy to absorb water and react. After coating, if the storage environment humidity is large, the surface coating of the pole film will also quickly absorb moisture in the air.
1.2 Electrolyte: the solvent component in the electrolyte will react chemically with water molecules; The solute lithium salt in the electrolyte is also easy to absorb water and undergo chemical reactions; So there will be a certain amount of water in the electrolysis; If the electrolyte storage time is too long, or the storage environment temperature is too high, the water content in the electrolyte will increase.
1.3 Separator: Separator is a porous plastic film (PP/PE material), and its water absorption is also very large.
2. Water added to electrode pulping
Negative pulping will add water to stir with raw materials, and then coating, so the negative sheet itself is water. In the subsequent coating process, although there is heating and drying, there is still a considerable part of water adsorbed inside the coating of the electrode sheet.
3. Workshop environment Moisture
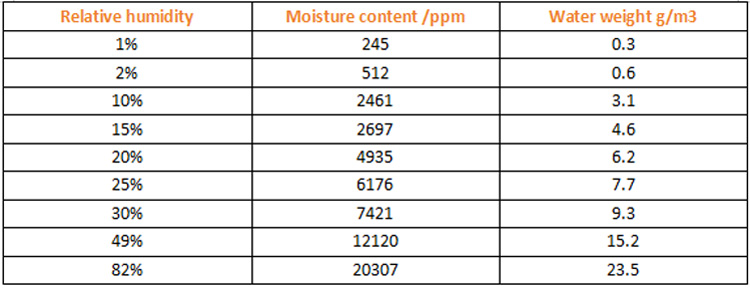
3.1 Moisture in the air in the workshop Moisture in the air is generally measured by relative humidity. The relative humidity varies greatly in different seasons and weather. The air humidity in spring and summer is relatively large (more than 60%), and the air in autumn and winter is relatively dry and the humidity is relatively small (less than 40%). The air humidity is higher in rainy days and lower in sunny days. So different air humidity, the water content in the air is different:
3.2 Water produced by the human body (human sweating, exhaled breath, water after washing hands)
3.3 Moisture brought in by various auxiliary materials and papers (cartons, rags, reports)
03. Water control in the production process of lithium batteries
1. Strictly control the environmental humidity of the production workshop
1.1 Homogenate stirring in the electrode production workshop, the relative humidity is ≦10%;
1.2 Coating (head, tail), roll dew point humidity ≤ -10℃DP in electrode production workshop;
1.3 Electrode production workshop cutting, relative humidity ≤ 10%;
1.4 Laminating, winding, assembly workshop, dew point humidity ≦-35℃ DP
1.5. Battery injection, sealing, dew point humidity ≤ -45℃ DP.
2. Strictly control the human body and external moisture brought into the workshop
2.1 Operation compliance management :
-- When entering the drying workshop, it is necessary to change clothes, wear hats, change shoes and wear masks;
-- It is forbidden to touch electrode sheets and electric cells with bare hands;
2.2 Moisture management of auxiliary materials:
-- It is strictly prohibited to bring the carton into the drying workshop;
-- The paper Posting and identification plates in the drying room shall be plastic sealed;
-- It is forbidden to mop the floor with water in the drying room.
3. Strictly control the storage and exposure time of electrode sheets
3.1 Management of low-humidity storage:
-- The rolled and cut electrode sheets must be stored in low-humidity environment within 30 minutes (≦-35℃ DP)
-- The baked and unmade electrode sheets must be vacuumed for storage (≦-95kpa)
3.2 Management of exposure time:
-- After baking, production, winding, packaging, liquid injection, sealing must be completed within 72h (workshop dew point humidity ≤ -35℃)
3.3 first-in first-out management:
-- The use of electrode sheets must follow the first-in first-out regulations, that is, the batch is used before; Bake first, use first.
4. Strictly control the baking process of the electrode sheet and separator
4.1 Before use, the electrode sheet and separator must be baked before use;
4.2 If the electrode sheet and separator cannot be baked before the production and winding, the cell must be baked before the liquid injection;
4.3 During the baking process of electrode sheet or battery cell, the oven parameters (temperature, time, vacuum degree) must be strictly monitored;
4.4 Oven temperature and vacuum degree shall be checked regularly to ensure accuracy.
5. Water content test and control
5.1 Electrode sheet, separator (or battery), electrolyte must test the water content, qualified to inject liquid;
5.2 Test method: sampling according to regulations; Use Karl Fischer moisture tester to measure;
5.3 Water content qualification standard:
-- electrode plate water content ≦200ppm (pre-control ≦150ppm)
-- separator water content ≦600ppm
-- electrolyte water content ≦20ppm

In summary, in the manufacturing process of lithium batteries, the moisture control of the environmental humidity, the storage and exposure time of the electrode, the baking process of the electrode and the separator, the validity period of the electrolyte, the water content test and other aspects are essential, once out of control, it will lead to fatal defects in the performance of the batch battery, and the consequences are very serious!
Therefore, whether it is management personnel, production personnel, quality inspection personnel, to strengthen the awareness of battery water control, always strictly abide by the provisions of the process, to ensure that the battery water has been in a controlled and qualified state!