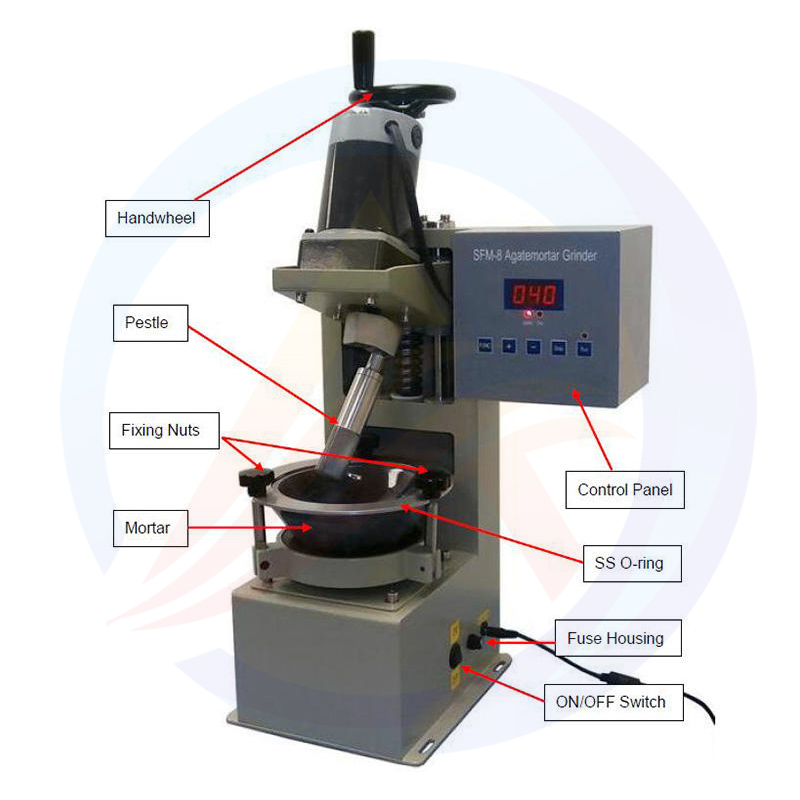
Lithium Battery Ball Mill Operation Guide
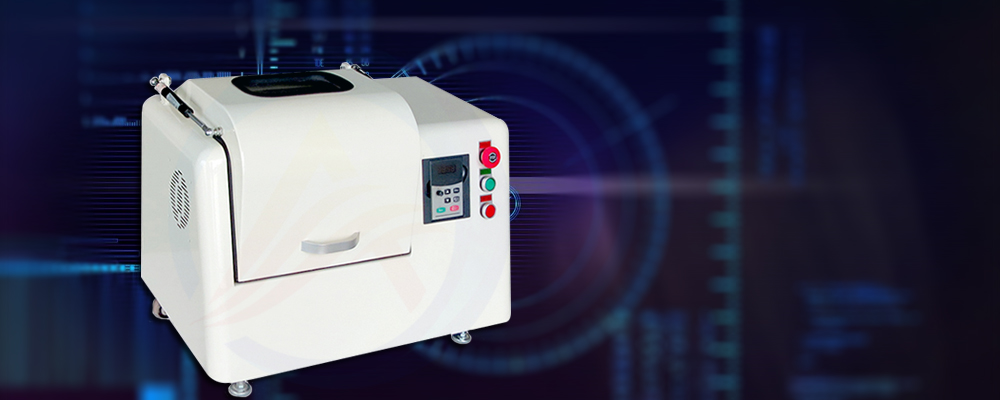

This operating guide is designed to provide operators with the operating procedures of lithium battery ball mills, introduce the main components of ball mills, and precautions. The ball mill is a critical piece of equipment in the lithium battery manufacturing process, used to mix and grind various raw materials to achieve the desired particle size and homogeneity for the battery's anode or cathode material.
I. Operation Guide
1. Preparation
Ensure that the ball mill and all necessary tools are clean and in good working condition.
Gather the required raw materials and ensure their quality and purity meet the specifications.
Prepare the ball mill media (e.g., steel balls) according to the manufacturer's recommendations.
2. Material Loading
Open the ball mill chamber and load the steel balls into the chamber.
Gradually add the raw materials into the chamber, ensuring that the material-to-ball ratio is within the recommended range.
Close the chamber securely and ensure all fasteners are tightened.
3. Operation
Power on the ball mill and set the desired rotation speed and grinding time based on the material properties and desired particle size.
Start the ball mill and monitor its operation throughout the grinding process.
Check for any abnormal noises, vibrations, or other signs of malfunction and take appropriate action if necessary.
4. Post-Grinding Process
Once the grinding process is complete, turn off the ball mill and allow it to cool down.
Open the chamber and carefully remove the ground material using a suitable scoop or shovel.
Separate the ground material from the steel balls and inspect the material for any impurities or unground particles.
5. Cleaning and Maintenance
Thoroughly clean the ball mill chamber and all accessories to remove any residual material or debris.
Inspect the steel balls for wear and replace any damaged or worn-out balls.
Perform regular maintenance tasks, such as lubricating the moving parts and checking the fasteners, according to the manufacturer's recommendations.
6. Safety Considerations
Always wear appropriate safety equipment, such as gloves, safety glasses, and protective clothing, while operating the ball mill.
Avoid direct contact with the rotating parts of the ball mill to prevent injuries.
Ensure that the power supply is properly grounded and that there are no electrical hazards in the work area.
7. Quality Control
Perform regular quality checks on the ground material to ensure it meets the desired specifications.
Adjust the grinding parameters, such as rotation speed and grinding time, if necessary, to optimize the quality of the ground material.
By following these steps and safety considerations, you can safely and effectively operate a lithium battery ball mill to produce high-quality materials for lithium battery manufacturing.
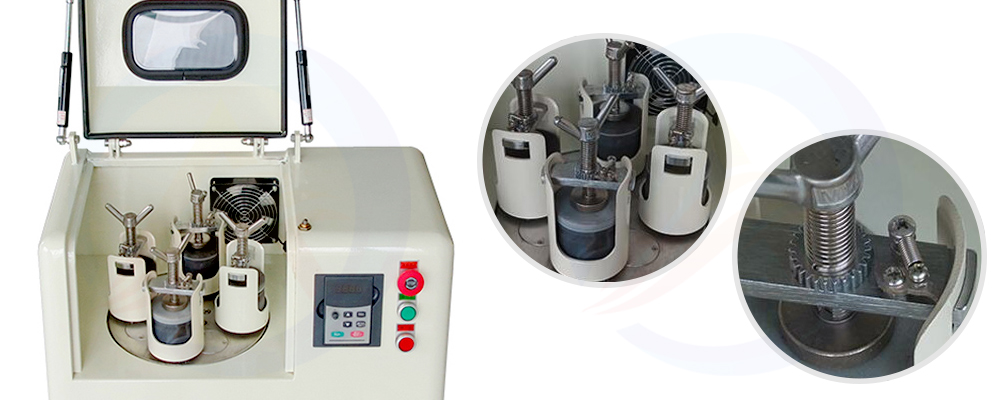

II. Components Overview
The lithium-ion battery ball mill is a crucial piece of equipment in the manufacturing process of lithium-ion battery materials. It comprises several components that work together to efficiently grind and mix the raw materials into a desired consistency. Here is an overview of the key components of a lithium-ion battery ball mill:
1. Feeding Device
Function: Responsible for feeding the raw materials into the ball mill in a uniform and controlled manner.
Description: Ensures consistent material flow for efficient grinding.
2. Hollow Shaft
Function: Supports the mill cylinder and allows the passage of materials and grinding media.
Characteristic: Designed with a hollow center to reduce weight and allow for the flow of water or slurry.
3. End Covers
Function: Closes the ends of the mill cylinder, protecting the internal components from external elements.
Features: Often equipped with feed and discharge ports, as well as inspection holes for maintenance.
4. Mill Cylinder
Function: The main working chamber where the grinding media (e.g., steel balls) and materials are mixed and grinded.
Characteristic: Cylindrical shape with wear-resistant lining installed on the inner wall to enhance durability.
5. Lining Plates
Function: Installed on the inner wall of the mill cylinder to prevent direct wear by the materials and grinding media.
Material: Typically made from wear-resistant materials like high manganese steel or rubber.
6. Drive System
Function: Powers the rotation of the mill cylinder, causing the grinding media and materials to move relative to each other for grinding.
Components: Includes motors, gearboxes, and other transmission mechanisms.
7. Discharge Device
Function: Responsible for discharging the ground materials from the ball mill.
Design: Can vary depending on the specific mill design and material discharge requirements.
8. Lubrication System
Function: Ensures proper lubrication of critical components like the main bearings to reduce wear and friction.
Components: Includes oil pumps, reservoirs, pipelines, and other related components.
9. Control System
Function: Provides automated control and monitoring of the ball mill's operation.
Components: Includes sensors, control panels, PLCs, and other electronic components.
These are the main components of a lithium-ion battery ball mill. Each component plays a crucial role in ensuring the efficient and reliable operation of the equipment.
III. Essential Considerations for Lithium-ion Battery Ball Mills
When operating a lithium-ion battery ball mill, there are several crucial considerations that must be taken into account to ensure safe, efficient, and reliable operation. Here are some essential points to keep in mind:
1. Safety Precautions
Always wear protective equipment such as safety glasses, gloves, and earplugs to protect yourself from potential hazards.
Ensure that all guards and safety devices are in place and functioning properly before starting the ball mill.
Avoid any direct contact with the rotating parts of the ball mill to prevent injuries.
2. Equipment Inspection
Perform regular inspections of the ball mill and its components to identify any potential issues or wear and tear.
Check the lubrication system regularly to ensure proper lubrication of critical components like the main bearings.
Monitor the wear of the lining plates and grinding media (e.g., steel balls) and replace them when necessary.
3. Material Handling
Use the correct feeding device to ensure a uniform and controlled feed of materials into the ball mill.
Avoid overloading the ball mill to prevent excessive wear and tear on the components.
Regularly clean the feed and discharge ports to prevent clogging or material buildup.
4. Operational Parameters
Monitor the operational parameters of the ball mill, such as the rotation speed, power consumption, and temperature.
Adjust the operational parameters accordingly to optimize the grinding efficiency and product quality.
Regularly check and adjust the grinding media load and composition to achieve the desired grinding effect.
5. Maintenance and Repairs
Schedule regular maintenance checks and repairs to keep the ball mill in good working condition.
Follow the manufacturer's instructions for maintenance and repair procedures to avoid damaging the equipment.
Use only genuine parts and components to ensure compatibility and durability.
6. Environmental Considerations
Ensure that the ball mill is properly ventilated to reduce dust and noise pollution.
Collect and dispose of dust and waste materials in accordance with local environmental regulations.
Use dust-control measures such as dust collectors or exhaust systems to minimize dust emissions.
7. Training and Awareness
Provide training to operators on the safe and proper operation of the ball mill.
Ensure that operators are aware of the potential hazards and safety precautions related to the ball mill.
Encourage operators to report any issues or concerns immediately to ensure prompt resolution.
By considering these essential points, you can ensure the safe, efficient, and reliable operation of your lithium-ion battery ball mill, maximizing its performance and longevity.